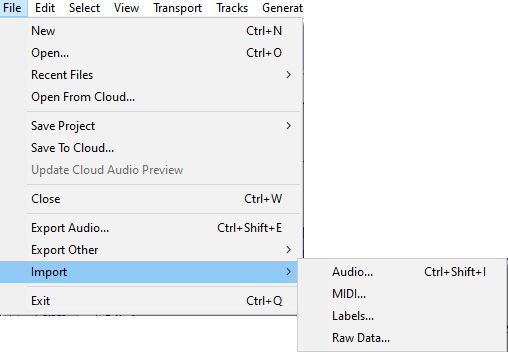
File Menu: Import
For audio files, the importer used depends on the currently selected file type in or and on settings in Extended Import Preferences.
See Importing Audio for more information.
Audio Ctrl +Shift + I
Launches a file selection window where you can choose to import one or more audio files into the current Audacity project. The file(s) will always be added as a new track to the project. This lets you mix two or more files together.
See Importing Audio for more information.
| Audacity supports multiple tracks with different sample rates.
The "Project Sample Rate" is the rate that the project is working in. If you have a project with two tracks, one with a sample rate of 8000 Hz and one with a sample rate of 48000 Hz, and the "Project Sample Rate" is set to 44100 Hz (default), then:
|
MIDI
Imports a MIDI (MIDI or MID extension) or Allegro (GRO) file to a Note Track where the Note track can be played.
This should just work on Windows but for playback on Mac and Linux additional software may be required, see this section on the Playing and Recording page.
Simple cut-and-paste edits can also be performed. The result can be exported with the command.
Labels
Launches a file selection window where you can choose to import a single text file into the project containing point or region labels. For more information about the syntax for labels files, see Importing and Exporting Labels.
Raw Data
Attempts to import an uncompressed audio file that might be "raw" data without any headers to define its format, might have incorrect headers or be otherwise partially corrupted, or might be in a format that Audacity is unable to recognize. Raw data in textual format cannot be imported.
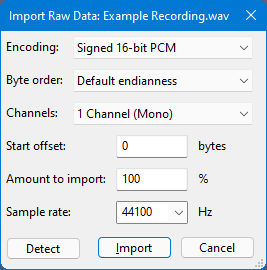
First, select the file in question in the "Select any uncompressed audio file" dialog.
Then use the button to let Audacity make a guess as to what kind of data your file is. If you know what kind of data you're dealing with, or if Audacity misidentified the format, you can set the following parameters yourself as well:
- Encoding (PCM, ADPCM, float...)
- Byte order (this is almost always Little-endian if the file was created on Windows)
- Number of channels (expected to be found in the file and created as a result)
- Start offset in bytes
- Percentage amount of the file to import
- Sample rate to be applied to the import (currently, rates between 100 Hz and 384,000 Hz are supported)