High-Pass Filter
From Audacity Development Manual
High-Pass Filter passes frequencies above its cutoff frequency and attenuates frequencies below its cutoff frequency. This effect can therefore be used to reduce low frequency noise.
Note carefully that when you apply an effect to a time-stretched clip the changed speed of the clip will be automatically rendered.
|
- Accessed by:

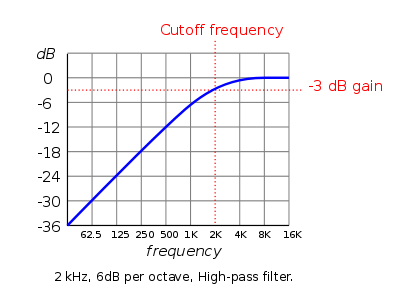
Frequency (Hz)
Sound below this cutoff frequency in Hz is not eliminated but increasingly attenuated as the frequency falls further below the cutoff.
The cutoff frequency (sometimes also called corner frequency) defines the point at which the audio is reduced by 3 dB. Thus there will also be a small and decreasing amount of attenuation just above the cutoff frequency as in the following image.
Roll-off (dB per octave)
Roll-off sets the steepness of the attenuation below the corner frequency. Higher roll-off values give a steeper slope to the attenuation. For example, with a roll-off of 6 dB per octave, the sound decreases by 6 dB in amplitude for each octave below the cutoff frequency (an octave above is double the frequency).
| To achieve more attenuation, run the effect again or use a greater roll-off. |